xanax reviews Tablets Uses, Dosage, Side Effects & Warnings
Table of Contents
what is xanax
Generic drug of the therapeutic class: Neurology–psychiatry
active ingredients: Alprazolam
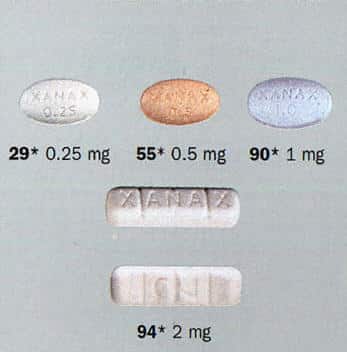
what is xanax used for and indication?
- Symptomatic treatment of severe and / or disabling anxiety disorders.
- Prevention and treatment of delirium tremens and other manifestations of alcohol withdrawal.
The 1 mg dosage is reserved for second-line treatment after failure of lower dosages.
Xanax Dosage
The use of alprazolam is not recommended in children, in the absence of study. In addition, the tablet is not a form suitable for children under 6 years (risk of mis-driving).
Oral way.
Dosage 0.25 mg is particularly suitable for the elderly, the renal or hepatic insufficiency.
– Dose :
In all cases, treatment will be initiated at the lowest effective dose and the maximum dose of 4 mg / day will not be exceeded.
. In general, in adults
treatment will be started at a dosage of 0.75 mg to 1 mg per day, divided into 3 doses as follows:
- 0.25 mg in the morning and at noon, and 0.25 mg in the morning. 0.50 mg in the evening.
- The dosage will then be individually adapted according to the therapeutic response.
- The average dosage is between 1 and 2 mg per day.
. In children, the elderly, the renal or hepatic insufficiency :
it is recommended to reduce the dosage, by half for example.
– Duration :
- . The treatment should be as short as possible.
- The indication will be reviewed regularly especially in the absence of symptoms.
- The overall duration of treatment should not exceed 8 to 12 weeks for the majority of patients, including the dose reduction period (see section on warnings and precautions for use).
- In some cases, it may be necessary to prolong the treatment beyond the recommended periods. This requires accurate and repeated assessments of the patient’s condition.
. Prevention and treatment of delirium tremens and other manifestations of alcohol withdrawal :
- short treatment of the order of 8 to 10 days.
Contraindications
CONTRA-INDICATE:
- This drug should never be used in the following situations:
- hypersensitivity to the active principle or to one of the other constituents.
- Severe respiratory insufficiency.
- syndrome of sleep apnea.
- severe hepatic insufficiency, acute or chronic (risk of encephalopathy occurred).
- myasthenia gravis.
- The tablet is not a suitable form for children under 6 years old (risk of aspiration).
- Due to the presence of lactose , this drug is contraindicated in cases of congenital galactosemia, glucose and galactose malabsorption syndrome or lactase deficiency.
NOT RECOMMENDED :
- Breast-feeding: the use of this medication during breast-feeding is not recommended.
- Avoid taking alcoholic beverages and drugs containing alcohol.
how does xanax work
ANXIOLYTICS ,
ATC Code: N05BA12 .
(N: central nervous system)
Alprazolam belongs to the class of 1-4 benzodiazepines and has a pharmacodynamic activity qualitatively similar to that of other compounds of this class:
- · Muscle relaxant,
- · Anxiolytic,
- · Sedative,
- · Hypnotic,
- · Anticonvulsant,
- · Amnesia.
These effects are related to a specific agonist action on a central receptor belonging to the complex “GABA-OMEGA macromolecular receptors”, also called BZ1 and BZ2 and modulating the opening of the chlorine channel.
what are the side effects of xanax?
They are related to the dose ingested, the individual sensitivity of the patient.
– Adverse neuropsychiatric (see warnings and precautions) :
- . anterograde amnesia, which may occur at therapeutic doses, the risk increasing the dose proportionally
- . behavioral disorders, alterations of consciousness, irritability, aggression, agitation,
- . physical and psychic dependence, even at therapeutic doses with withdrawal symptoms or rebound upon discontinuation of treatment
- . lightheadedness, headache, ataxia
- . confusion, drowsiness or decrease alertness (particularly in the elderly), insomnia, nightmares, tension
- . changes in libido.
– Cutaneous side effects :
- rashes, itchy or not.
– General side effects :
- muscle hypotonia, asthenia.
– Ocular adverse effects :
- diplopia.
– Hepatic side effects :
- very rare cases of increase in liver enzymes, jaundice, cytolytic or cholestatic hepatitis.
Xanax Interactions
Associations advised against
what is the interaction between xanax and Alcohol?
- Alcohol enhancement of the sedative effect of benzodiazepines and the like. Altered alertness can make driving dangerous and the use of machinery dangerous.
- Avoid taking alcoholic drinks and drugs containing alcohol.
Associations to consider
Other central nervous system depressants:
- Morphine derivatives (analgesics, antitussives and substitution treatments other than buprenorphine); neuroleptics including clozapine; barbiturates; other anxiolytics; hypnotics; sedative antidepressants; sedative antihistamines H1; central antihypertensives; baclofen; thalidomide; pizotifene.
- Increase of the central depression. Altered alertness can make driving dangerous and the use of machinery dangerous.
- In addition, for morphine derivatives (analgesics, antitussives and substitution treatments), barbiturates: increased risk of respiratory depression, especially present in the elderly, which can be fatal in case of overdose.
what is the interaction between xanax and Clozapine?
- Increased risk of collapse with respiratory and / or cardiac arrest.
what is the interaction between xanax and Buprenorphine?
- With buprenorphine used in substitution therapy: increased risk of respiratory depression, which can be fatal.
- Carefully evaluate the benefit / risk ratio of this combination. Inform the patient of the need to respect the prescribed doses.
Xanax Warnings and Precautions :
what is xanax warning?
This medicine contains lactose. Its use is not recommended in patients with intolerance to galactose, a deficiency of lapp lactase or a syndrome of glucose or galactose malabsorption (rare hereditary diseases).
PHARMACOLOGICAL TOLERANCE:
The anxiolytic effect of benzodiazepines and related substances may decrease gradually despite the use of the same dose when administered for several weeks.
ADDICTION :
Any treatment with benzodiazepines and related drugs, especially with prolonged use, may result in a state of physical and mental dependence.
Various factors seem to favor the occurrence of dependence:
- Duration of treatment,
- Dose,
- History of other drug addictions, including alcoholic.
Drug dependence may occur at therapeutic doses and / or in patients without individualized risk factors.
In case of physical dependence, a sudden cessation of treatment may lead to withdrawal symptoms. These symptoms may be: insomnia, headache, myalgia, significant anxiety, nervous tension, impatience, confusion, irritability. In severe cases, the following symptoms may occur: derealization, depersonalization, hyperacusis, numbness and tingling of the extremities, hypersensitivity to light, noise and physical contact, hallucinations, epileptic seizures.
Withdrawal symptoms may occur within days of stopping treatment. For short-acting benzodiazepines, and especially if given at high doses, symptoms may even occur in the interval between two doses.
The combination of several benzodiazepines, regardless of the anxiolytic or hypnotic indication, may increase the risk of drug dependence.
The risk of withdrawal is greater when the drug is stopped abruptly, it is recommended to gradually reduce the daily dose (see section Warnings and precautions for use , precautions for use, Duration and methods of stopping progressive treatment).
Cases of abuse have been reported.
REBOUND OF ANXIETY:
- This transient syndrome, whose symptoms initially motivated treatment with benzodiazepines, can be exacerbated when treatment is stopped.
- This syndrome can be accompanied by other reactions including mood changes, anxiety and sleep disorders and impatience.
- As the risk of a rebound phenomenon is greater when stopping the drug is abrupt, it is recommended to gradually reduce the daily dose (see section Warnings and precautions for use , precautions for use, duration and methods of stopping progressive treatment).
AMNESIA AND ALTERATIONS OF PSYCHOMOTIC FUNCTIONS:
- Anterograde amnesia and alterations of the psychomotor functions are likely to appear in the hours following the taking.
PSYCHIATRIC AND PARADOXAL REACTIONS:
- In some subjects, benzodiazepines and related products may result in a syndrome associating to varying degrees an impairment of consciousness and behavioral and memory disorders:
Can be observed:
- Worsening of insomnia, nightmares, agitation, nervousness;
- Delusions, anger, hallucinations, confuso-oniric state, psychotic symptoms;
- Disinhibition with impulsivity;
- Euphoria, irritability, aggressiveness;
- Anterograde amnesia;
- Suggestibility.
- Impatience
This syndrome may be accompanied by potentially dangerous disorders for the patient or for others, such as:
- Unusual behavior for the patient;
- Self- or hetero-aggressive behavior, especially if the family is trying to interfere with the patient’s activity;
- Automatic driving with post-event amnesia.
These events require the cessation of treatment.
These behavioral disorders may occur more in children and elderly patients.
RISK OF ACCUMULATION:
Benzodiazepines and related drugs (like all drugs) persist in the body for a period of about 5 half-lives (see section Pharmacokinetic properties ).
In the elderly or with renal or hepatic insufficiency, the half-life may be considerably longer. When taken repeatedly, the drug or its metabolites reach the equilibrium plateau much later and at a much higher level. It is only after obtaining a balance plateau that it is possible to evaluate both the efficacy and the safety of the drug.
Dosage adjustment may be necessary (see section Dosage and method of administration ).
SUBJECT AGE:
- Benzodiazepines and related products should be used with caution in the elderly, because of the risk of sedation and / or myorelaxant effect that may lead to falls, with often severe consequences in this population.
- It is recommended to use the lowest effective dose in the elderly and / or the weakened subject to avoid the occurrence of excessive ataxia or sedation (see section Dosage and method of administration ).
what is a precaution when taking xanax?
Great caution is advised in case of a history of alcoholism or other addictions, drug or not (see section Interactions with other drugs and other forms of interaction ).
AT THE SUBJECT HAVING A MAJOR DEPRESSIVE EPISODE:
Benzodiazepines and related drugs should not be used alone to treat depression because they cause or increase the risk of suicide. Thus, alprazolam should be used with caution and its prescription should be framed in patients with signs and symptoms of depressive disorder or suicidal tendencies.
DURATION AND PROCEDURES FOR PROGRESSIVE STOPPING OF TREATMENT (see section Dosage and method of administration ):
- The treatment should be as short as possible.
- At the beginning of treatment, it may be useful to inform the patient that the duration of treatment will be limited.
- The modalities of gradual cessation of treatment must be stated to the patient in a precise manner.
- In addition to the need for gradual decrease in doses, patients should be warned of the possibility of a rebound phenomenon, to minimize the anxiety that may arise from the symptoms related to this interruption, even progressive.
- The patient must be warned of the possibly uncomfortable nature of this phase.
- With prolonged use of long-acting benzodiazepines, it is important to warn against switching to a short-acting benzodiazepine, withdrawal symptoms may occur.
SUBJECT AGE, INSUFFICIENT RENAL, INSUFFICIENT HEPATIC:
- Benzodiazepines and related products should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment or mild to moderate hepatic impairment.
- The risk of accumulation leads to a reduction in the dosage, for example by half (see section Dosage and method of administration ).
INSUFFICIENT RESPIRATORY:
- In patients with respiratory insufficiency, the depressant effect of benzodiazepines and related substances should be taken into account (especially since anxiety and agitation may be signs of a call for a decompensation of the respiratory function which justifies the transition to intensive care unit).
CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS:
- The safety and efficacy of alprazolam have not been studied in children and adolescents under 18 years of age. Its use is not recommended in this population.
Drive and use machines
- Prevent drivers of vehicles and machinery users from the risk of drowsiness, damnation or impaired muscle concentration or function.
- Combination with other sedating medicinal products should be discouraged or taken into account when driving or using machines.
- If sleep time is insufficient, the risk of impaired alertness is further increased.
Xanax with PREGNANCY and BREAST FEEDING
how does xanax affect pregnancy?
- Many data from cohort studies have not revealed the occurrence of malformative effects during benzodiazepine exposure during the course of 1 first trimester of pregnancy. However, in some case-control epidemiological studies, an increase in the occurrence of cleft lip and palate has been observed with benzodiazepines. According to these data, the incidence of cleft lip and palate in newborns would be less than 2/1000 after exposure to benzodiazepines during pregnancy while the expected rate in the general population is 1/1000.
- If benzodiazepines are taken in high doses at 2 nd and / or 3 rd trimesters of pregnancy, a decrease in fetal active movements and a variability in fetal heart rate have been described. Treatment with benzodiazepines at the end of pregnancy, even at low doses, may be responsible in the newborn for signs of impregnation such as axial hypotonia, sucking disorders resulting in low weight gain. These signs are reversible, but can last 1-3 weeks depending on the half-life of the prescribed benzodiazepine. At high doses, respiratory depression or apnea, and hypothermia may occur in the newborn. In addition, a neonatal withdrawal syndrome is possible, even in the absence of signs of impregnation. It is characterized in particular by hyperexcitability, agitation and tremulations of the newborn occurring at a distance from the delivery.
- The time of onset depends on the elimination half-life of the drug and may be important when it is long.
- Based on these data, as a precautionary measure, the use of alprazolam is not recommended during pregnancy, regardless of the term.
- When prescribing alprazolam to a woman of childbearing potential, she should be advised of the need to contact her physician if pregnancy is planned or initiated to re-assess the benefit of the treatment.
- At the end of pregnancy, if it is really necessary to start a treatment with alprazolam, avoid prescribing high doses and take into account, for surveillance of the newborn, effects previously described.
Breastfeeding
Immediately consult your doctor or pharmacist.
What is Forms and Composition Xanax ?
| FORMS and PRESENTATIONS |
- 0.25 mg scored tablet: Box of 30, in blister packs.
- Hospital model: Box of 100. 0.50 mg scored tablet: Box of 30, in blister packs. Hospital model: Box of 100. Breakable tablet 1 mg: Box of 100, in blister packs.
| p cp | |
| Alprazolam (DCI) | 0.25 mg |
| or | 0.50 mg |
| or | 1 mg |
- Excipients (common): lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, anhydrous colloidal silica, mixture of sodium docusate (85%) and sodium benzoate (15%), corn starch, magnesium stearate, aluminum erythrosine lake (cp 0 , 50 mg and 1 mg), indigo aluminum lake (cp 1 mg).
NOT’s
Edrug-online contains comprehensive and detailed information about drugs available in the medical field, and is divided into four sections:
general information:
- Includes a general description of the drug, its use, brand names, FAQs, and relevant news and articles
Additional information:
- General explanation about dealing with the medicine: how to take the medicine, the doses and times of it, the start and duration of its effectiveness, the recommended diet during the period of taking the medicine, the method of storage and storage, recommendations in cases for forgetting the dose and instructions to stop taking the drug and take additional doses.
Special warnings:
- For pregnant and breastfeeding women, the elderly, boys and drivers, and use before surgery.
Side effects:
- It treats possible side effects and drug interactions that require attention and its effect on continuous use.
- The information contained in this medicine is based on medical literature, but it is not a substitute for consulting a doctor.
